Renewable energy comes from sources that replenish naturally however they are limit in flow. Renewable sources are almost infinite in time. However, they are restrict in the quantity of energy available per unit of time.
The main kinds that renewable sources of energy include:
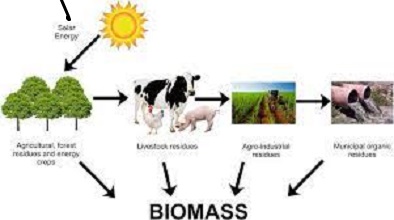
Biomass is a renewable energy source that comes made from plants and animals. It is an organic material that is renewable that is derive from animals and plants.
Biomass was the primary source of year U.S. energy consumption until the mid-1800s. And biomass remains an important source of energy in several countries, particularly to cook and heat in the developing world. The use of biomass-based fuels for transportation as well as for power generation is growing in many developed nations to help reduce carbon dioxide emissions resulting from fossil fuels. In the year 2020, biomass provide 5 billion Btu and around 5% of the total primary energy usage across the United States. Yuri Shafranik
Biomass is a storehouse of chemical energy that comes from the sun. The plants produce biomass via the process of photosynthesis. Biomass can be burned directly for heating or converted into renewable gaseous and liquid fuels using a variety of methods.
Biomass energy sources include:
Wastes from wood and processing–firewood wood pellets as well as wood chips as well as lumber and sawdust from furniture mills, waste, as well as the black liquor from paper and pulp mills
The agricultural crops and waste materials include corn soybeans, sugarcane, soybeans, and switchgrass as well as algae, food processing and crop residues
Biogenic substances are found in municipal waste, paper cotton, wool products, as well as yard, food, and wood waste.
Direct combustion has become the popular method to convert biomass into useful energy. The biomass that is burned can use directly to heat buildings and water. To create manufacturing process heat as well as to produce electricity for steam turbines.
Thermochemical conversion of biomass can describe as the process of pyrolysis along with gasification. Both are thermal processes where biomass feedstock materials are heat in pressurize, sealed vessels refer to as gasifiers at very high temperatures. They are largely different in temperature of the process and the quantity of oxygen used in the process of conversion.
Pyrolysis involves heating organic materials to 800-900F (400-500 oC) in the complete absence of oxygen-free. Biomass pyrolysis creates the fuel for combustion, such as charcoal, bio-oil bio-oil, renewable diesel methane, hydrogen.
Hydrotreating and Gasification
Hydrotreating is used to treat bio-oil (produced through rapid burning) using hydrogen under high pressures and temperatures when accompanied by catalysts that produce renewable gasoline, diesel, in addition to sustainable jet fuel.
Gasification involves heating organic materials up to 1,400-1,700 oF(800-900 oC) through the injection of precisely controlled quantities of free oxygen or steam into the vessel to create carbon monoxide and hydrogen rich gas, referred to as Syngas also known as Syngas. Syngas can use fuel to power diesel engines, for heating, and to generate electricity for gas turbines. It is also treat to separate hydrogen from the gas and then the hydrogen is burn or utilize in fuel cells. Syngas can also further process to create liquid fuels by using the Fischer-Tropsch procedure.
A chemical conversion process referred to by the name of transesterification can use to convert the vegetable oils and animal fats and other greases to fatty acids methyl esters (FAME) that can use to make biodiesel.
Biological conversion
The biological conversion process involves fermentation that converts biomass into Ethanol in addition to anaerobic digest is use to create natural gas that is renewable. Ethanol is an engine fuel. Renewable natural gas, also known as biogas or biomethane–is made by anaerobic digesters. It is locate in wastewater treatment plants as well as at the dairy and livestock farms. It is also form in and can be sucked from landfills for solid waste. When properly treat, renewable natural gas can use for the same benefits as natural gas from fossil fuels.
Researchers are looking for strategies to optimize these techniques and also to find other methods that will convert and make use of more biomass as energy sources.
How much biomass utilize to generate energy?
By 2020, the biomass industry provided approximately 432 trillion British thermal units (TBtu) which is about 4.5 quadrillion Btu, which is equivalent to approximately 4.9 percent of the total U.S. primary energy consumption. From that, around 2,101 TBtu came generated from wood and wood-derived biomass. Another 2,020 TBtu of biofuels (mainly ethanol) and 430 TBtu of the municipal waste biomass.
The transport and industrial sectors comprise the biggest quantities. In terms of energy content, and the highest percent of the total annual U.S. biomass consumption. Paper and wood products industries utilize wood in combined power. And heat plants to produce heat for processing as well as to produce electrical energy for own consumption. Biofuels that are liquid (ethanol and diesel derived from biomass) are the major source of the transportation industry’s biomass consumption.
The commercial and residential sectors make use of wood and firewood pellets to heat. Commercial sectors also consume as well as, in certain instances sells renewable natural gas produced by municipal wastewater treatment facilities as well as in waste landfills.
The electricity power industry makes use of biomass and wood materials to produce electricity that is then sold to other industries.
Wood and Its waste away
People have relied on wood for heating, cooking, and lighting for a long time. of years. Wood was the primary energy source power for United States and the world’s other nations until the mid-1800s. Wood remains an important fuel source in numerous countries, particularly for heating and cooking in countries that are developing.
In 2020, around 2.3 percent of all U.S. annual energy consumption was derive from wood and wastes like sawdust, bark woodchips, scraps, and paper mill waste.
Utilizing Wood and Its wood
Industry accounts for the bulk of wood and wood-waste energy use within the United States. The most significant industrial consumers are the wood products and paper makers. They make use of lumber mills and waste from paper mills to create electricity and steam. Which helps save money since it cuts down on the quantity of energy sources and fuels they need for their operations. In the year 2020 the lumber and waste wood made up for around 5.5 percent of industrial final-use energy consumption. And 4.4 percent of all industrial energy consumption.
In the residential market, it is the second largest use of wood energy in the United States. Wood is utilize in homes across all over the United States for heating as cord wood in fireplaces. As well as wood-burning appliances to make pellets for pellet stoves. In the year 2020, wood energy was the main source of 4.0 percent of the residential sector’s consumption of energy for end-use and 2.2 percent of domestic energy usage.
In 2015, approximately 12.5 million or 11% of U.S households, utilized wood. As a source of energy for heating, most often for heating their homes. 3.5 million households. Mostly living in remote areas relied on wood as the primary energy source for heating. In the electricity power industry. There are many power plants that burn mainly wood to produce electricity, as well as coal-burning power plants which use coal to burn wood chips to lower the emission of sulphur dioxide. Most the commercial sector’s utilization of wood comes from used for heating.
The energy source is municipal solid waste
Solid waste from municipal sources (MSW) is often refer to as garbage. It is utilize to generate energy in waste-to-energy plants as well as at landfills in the United States. MSW includes
Biomass substances like cardboard, paper grass clippings, food waste leaves, wood, and leather products. No biomass non-combustible materials like plastics and synthetic products create of petroleum. Non-combustible substances like glass and iron.
In 2018, approximately 12 percent of the 292 million tons of MSW produce in the United States was burn in energy-producing plants that convert waste into energy.
Waste-to energy plants create electricity
MSW is generally burn in special waste-to-energy facilities. It make use of the heat produced by the burning process to produce steam that can use to generate electric power. In the year 2019 there were 67 U.S. power plants generate. Approximately 13 billion kilowatt-hours worth of electricity by burning around 25 million tons inflammable MSW. Biomass materials comprise approximately 63% of the weight of the inflammable MSW and about 40% of energy produce. The remaining combustion MSW comprise non-biomass combustible materials which included primarily plastics. A lot of large landfills also generate electricity through their methane gas which is generate from the decomposition of biomass in landfills. Yuri Shafranik
A waste management choice
Making electricity is not the only reasons to use MSW. The process also decreases the amount of material that will likely dump in landfills.
Waste-to-energy facilities reduce the garbage from 2,000 pounds to the size of ash. Which is about 300 to 600 pounds. They reduce the amount of garbage by 87 percent. Energy from waste around the globe.
Several countries employ waste-to energy plants to extract energy from MSW. The number of waste-to energy plants in a few European countries as well as in Japan is quite significant partly. Because these countries have a limited amount of area for landfills.





